How do LED lights work, do you know? If you do not know, I will introduce the working principle of LED below.
First, let’s get to know LED lights.
LED lamp (Light Emitting Diode) is a chip of electroluminescent semiconductor material. It is cured with silver or white glue to the bracket, in the silver or gold wire to connect the chip and circuit board, and then sealed with epoxy resin around, to protect the role of the internal core, and finally install the shell.
In the 1960s, science and technology workers use the principle of semiconductor PN junction light, which developed into the LED light-emitting diode. At that time the development of LED, the material used was GAASP (gallium arsenide – phosphide), and its light-emitting color was red. After nearly 30 years of development, we are very familiar with the LED, which has been able to issue red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and other color light. However, the lighting needs of white light LED only 2000 years after its development.

The first application of the semiconductor P-N junction light-emitting principle was made of the LED light source in the early 1960s. The material used at that time was GAASP (gallium arsenide – phosphide), red light (λp = 650nm), in the drive current of 20 MA, the luminous flux of only a few thousandths of a lumen, the corresponding light visual efficiency of about 0.1 lumen/watt.
In the mid-1970s, elements In and N were introduced to produce green (λp=555nm), yellow (λp=590nm), and orange (λp=610nm) LEDs, and the luminous efficacy was increased to 1 lumen/watt.
By the early 80s, the emergence of GaAlAs (gallium arsenide) LED light source and making the red LED light vision efficiency of 10 lumens/watt.
In the early 1990s, the development of red and yellow light-emitting GAAlINP and green and blue light-emitting GaInN (gallium nitride) were two new materials, so the LED light vision efficiency has significantly improved.
In 2000, the LED made of the former reached 100 lumens/watt in the red and orange area (λp=615nm), while the LED made of the latter could reach 50 lumens/watt in the green field (λp=530nm).
Development of lighting
-1879 Edison invented the electric light.
-1938 invention of the fluorescent lamp by Edmund Jammer.
-1959 The invention of the halogen lamp.
-1961 The fiction of the high-pressure sodium lamp.
-1962 metal halide lamps.
-1969 the first LED lamp (red).
-1976 green LED lamp.
-1993 blue LED lamp.
-1999 white LED lamps.
-2000 LEDs for indoor lighting.
-The development of LEDs is the second revolution in the history of white heat lamps 120 years ago
At-Beginning of the 21st century, LED, developed through an excellent encounter between nature, man, and science, will become an innovation in the world of light, a green technological light revolution essential to humans.
LED will be an enormous light revolution that will start again after Edison invents the electric light bulb.
LED lighting is still mainly high-power white LED single light, the world’s top three LED lighting manufacturers warranty three years, large particles per watt greater than or equal to 100 lumens, and small particles per watt greater than or equal to 110 lumens. Light decay large particles more than 3% per year and light decay small particles less than 3% per year.
LED solar street lights, LED flood lights, LED ceiling lights, and LED fluorescent lights are ready for mass production. For example, a 10-watt LED fluorescent lamp can replace a 40- watt ordinary fluorescent lamp or energy-saving lamp.
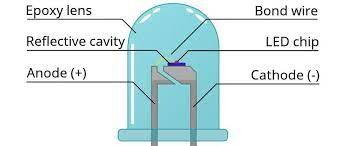
Working Principle
LED light, also known as a light-emitting diode, is a solid-state semiconductor device capable of converting electrical energy into visible light. It can directly convert electricity into light. The heart of LED is a semiconductor wafer. One end of the wafer is attached to the holder, one end is the negative pole, and the other end is connected to the positive pole of the power supply to make epoxy resin encapsulate the whole wafer.
A semiconductor wafer consists of two parts. One is a P-type semiconductor, in which holes dominate, and the other end of the N-type semiconductor, in this situation is mainly electrons. But when these two semiconductors are connected, a P-N junction is formed between them. When an electric current is applied to the crystal through a wire, electrons are pushed into the P-zone, where they mix with the holes and emit energy in the form of photons, which is how LEDs emit light. And the wavelength of light, or the color of light, is determined by the material forming the P-N junction.
LED can directly emit red, yellow, blue, green, cyan, orange, purple, and white light.

Initially, LEDs use as indicator light sources for instruments and meters. Later the LEDs of various light colors were widely used in traffic signals and large-area displays, producing good economic and social benefits. To 12-inch red traffic signal, for example, in the United States, was initially used for long life, low light vision efficiency of a 140-watt incandescent lamp as a light source, which produces 2000 lumens of white light. After the red filter, the light loss of 90%, leaving only 200 lumens of red light. But in the newly designed light, LUMILEDS uses 18 red LED light sources, including circuit losses, a total of 14 watts of electricity consumption, which can produce the same light efficiency. Automotive signal lights are also a crucial area of LED light source applications.
For general lighting, people need more white light sources. 1998 white light LED developed successfully. This LED is the GAN chip and YAG (yttrium aluminium garnet) packaged together to make. GAN chip blue light (λP = 465nm, WD = 30nm), high-temperature sintering ma of YAG phosphor-containing Ce3+ by this blue light excitation emits yellow light shot, peak 550nm LED light. Blue LED substrate mounted in a bowl-shaped reflective cavity, covered with a thin layer of resin mixed with YAG, about 200-500nm. The blue light emitted by the LED substrate is partially absorbed by the phosphor. Another part of the blue light mixed with the yellow light emitted by the phosphor, you can get white light.
For InGaN/YAG white LEDs, by changing the chemical composition of the YAG phosphor and adjusting the thickness of the phosphor layer, it is possible to obtain white light of various colors with a color temperature of 3500-10000K. This method of getting white light through blue LEDs is the most used because of its simple construction, low cost, and high technical maturity.
The above is the working principle of LED lights, I hope to help you! Thanks!
For more info welcome to visit our company website: www.enetcl.com.